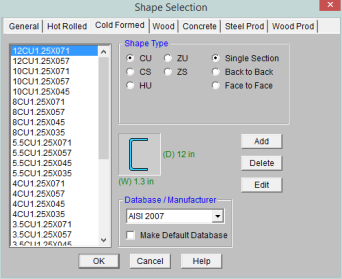
Shapes are organized in the database by manufacturer. Common shapes are supported such as C sections(with and without lips), Z sections(with and without lips), and Hat sections(without lips). Each of these shape types may be used as Single section, a Back-to-Back section, or a Face-to-Face section. You may type in the names directly, select shapes from these databases, or add your own shapes.
RISA currently supports the following common Cold Formed steel databases: AISI 2007, Dale-Incor, Dietrich, Marino-Ware, and SSMA.

To Select a Cold Formed Database Shape
 .
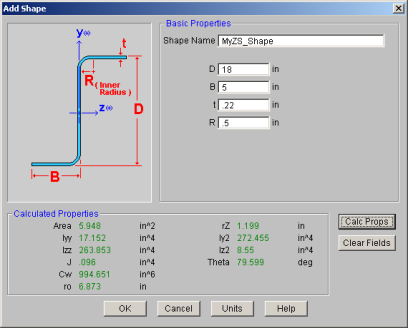
.You can enter your own cold formed shapes as well as use those provided in the manufacturer database. When the cold formed database type is selected, you'll notice a "Manufacturer" list box that appears in the Shape Selection dialog. You can specify a manufacturer or choose “Custom” to select, add or edit your own custom shapes. New shape properties are calculated using the linear method described in Part I of the AISI code.
The cold formed manufacturer shape databases are stored in the file aisidb32.fil, and the custom cold formed shapes are stored in the file aisicust.fil.
To Add a Database Shape
Note
There are five types of shapes. Names for each shape type follow
the convention of the manufacturer for each shape. If you know the
shape name, you can type the name directly into the Shape field
on the spreadsheets. Alternately you may click the 
For the AISI database, CU shapes are called out by the designation given them in the AISI steel manual. For example, if you wanted a 12" deep unstiffened C section, you'd call it out as 12CU1.25x071. The '12' is the depth, the CU specifies a C section without lips, the '1.25' is the flange width, and the '071' is the decimal thickness. Other manufacturer databases generally follow similar conventions.
For the AISI database, CS shapes are called out by the designation given them in the AISI steel manual. Other manufacturer databases generally follow similar conventions.
For the AISI database, ZU shapes are called out by the designation given them in the AISI steel manual. Other manufacturer databases generally follow similar conventions.
For the AISI database, ZS shapes are called out by the designation given them in the AISI steel manual. Other manufacturer databases generally follow similar conventions.
For the AISI database, HU shapes are called out by the designation given them in the AISI steel manual. Other manufacturer databases generally follow similar conventions.
For the AISI database, HU shapes are called out by the designation given them in the AISI steel manual. Other manufacturer databases generally follow similar conventions.
For each of the five shape types the selected shape may be used as a standard single section or as a double section. The choices for double sections are Back-to-Back and Face-to-Face. A typical double section is designated with a "2-" preceding the shape name and a "-BB" (Back-to-Back) or "-FF" (Face-to-Face) following the shape name. For example, a "2-12CU1.25x071-FF" section represents two 12" deep C sections with 1.25" wide flanges and a 0.071" thickness placed face-to-face.